A growing body of research recognizes the influences of religion and religious faith on human behavior and psychological functioning, particularly in adolescence [1]. Most university students are adolescence. Adolescence is a critical period of human development with rapid physical, psychosocial, cognitive, and emotional development, and sexual and reproductive maturation [2]. University students are vulnerable to unhealthy lifestyle behavior due to the nature of their academic life. Investing in university students’ health ensures triple dividends in terms of health during their adolescence, health during later adulthood as well as the health of the future generation [3].
Religious practice
The first line of debate of the present study is about university students’ or adolescents’ religious practice. In this study, religious practice means a practice related to the holding of a religious belief. Dew et al. [4] found that the measurement of religious practice varied across studies in kinds of literature, with most studies defining religious practice as church attendance, religious beliefs, religious affiliation, or religious importance. For the purposes of this study, religiosity is defined as one’s beliefs and practices related to any religious affiliation or to God or Allah. A number of studies have found different factors or forms for religiosity: (1) public religiosity and (2) private religiosity. Private religiosity—is characterized by diverse, flexible, less restrictive social interaction and quiet faith, and less explicit religious activity and participation [5, 6]. For instance, it contains praying alone, and rarely participating in religious events and practices. Public religiosity which is characterized by membership in a clearly defined group, an individual’s centralized denominational social identification but relatively rigid. Public religiosity is the type of religious practice most commonly studied in the empirical literature [6]. Religious involvement may benefit adolescents’ lives by empowering both internal (e.g., the feeling of self-worth), social (e.g., a sense of belonging to a network) resources [7], and leading to ethical decisions [8]. Religious education can be instrumental in improving adolescents’ healthy lifestyle behavior by developing religious morality, reinforcing religious coping, developing respect for religious diversity, and promoting connectedness. Religious affiliation played a role in making difference in religious practice (Christianity has a high mean of religious practice, and Islam has the opposite [9].
Healthy lifestyle behavior
A second line of debate in the present study is adolescents’ health lifestyle behavior. Healthy lifestyle behaviors are any determinants undertaken to prevent some kind of illness or to improve health and well-being [10]. The importance of the meaning of life in adolescent behavior is clearly reflected in human history [11]. Particularly, adolescence is a period when an individual develops the capacity to understand and internalize religion and its impact on their cognitive development. Adolescents are able to identify unhealthy lifestyles and healthy lifestyles. However, adolescents were engaged in healthy and unhealthy lifestyles simultaneously. This family, school, neighbors, and health care workers should work together and be vigilant in assessing and removing factors that prevent adolescents from adopting healthy lifestyles. Healthy lifestyle behavior include healthy eating, physical activity, sexual activity, and emotional well-being [12]; healthy physical and mental state (exercise, eating a healthy diet, and avoiding stress), vegetarian diet, no alcohol intake, an appropriate rest, increased recreational physical activity, development of their faith and hope, non-use of tobacco or other addictive substances.
Adolescents and young people are vulnerable to both a range of health risks and benefits [12]. Japar and Purwati [13] reported that the forms of adolescents’ unhealthy lifestyle behaviors are telling lies, going out without permission, staying up and talking all night, fighting with schoolmates, fighting with students, throwing trash anywhere, reading pornography books, watching pornography films, driving motorcycles/cars without driving licenses, driving at excessive speed, living together (out of matrimony), free sex, thieving, picking a pocket, committing armed robbery, abortion, rapping, killing. Health risks may affect adolescents immediately, such as infectious diseases, malnutrition, accidents, or sexually transmitted diseases, or in the future, such as cardiovascular diseases and cancers. These risks may originate as a result of their lifestyle and health status during adolescence [14].
Paweł et al. [10] identified four dimensions of lifestyle behaviors: Nutrition, prophylaxis (obeying health recommendations), positive attitude (avoiding emotional overload and stress situations), and pro-health practices (physical activity, good sleeping habits, and relaxation). However, there are currently other more popular approaches that consider multiple healthy lifestyle behavior. Thus, the present study uses a scale that measures university students’ healthy lifestyle behavior in various countries (e.g. in Saudi Arabia by Almutairi et al. [15]; in China by Wang et al. [16]; in Canada by Coulson et al. [17]. The dimensions of multiple healthy lifestyle behavior include: Healthy responsibility, nutrition, stress management, interpersonal relations, physical activity, and spiritual growth.
According to, Almutairi et al. [15], gender, type of college or university, and length of stay, or year in school were significant predictors of the healthy lifestyle of students in Saudi Arabia’s universities. Students in Saudi Arabia were found to have an inadequate level of adherence to recommendations regarding physical activity, and attend educational programs on health care and healthy nutrition habits. Coulson et al. [17] found that students had a lower level of stress, higher interpersonal relations, higher health responsibility, and better general spiritual health.
Relationship between religious practice, healthy lifestyle behavior, and academic achievement
A third line of debate of the present study is about the relationship between religious practice, healthy lifestyle behavior, and academic achievement. When we examine the relationship between, religious practice and healthy lifestyle behavior, globally, a growing body of research recognizes religious involvement as an important dimension in adolescent development [1, 11].
Over the last decades, some researchers have studied the association between religiosity in health maintenance [18,19,20,21,22,23]. In addition, other studies have found that healthy lifestyle behavior is associated with religion and planned activities in Australia [18], Asia [24], American and Czech [25, 26] adolescents. It has been observed that adolescents and young people involved in some religious affiliation exhibit healthier behaviors, such as participating more actively in extracurricular activities during their free time [27,28,29,30] and getting more involved in family and religious social interaction [30, 31] than those who do not.
Gonçalves et al. [32] also showed that religious and spiritual interventions have positive effects on mental health outcomes such as a significant decrease in stress, depression, and alcoholism. Religion is affecting individuals’ choices with respect to risky behaviors by protecting individuals from risky behaviors. In Danish society, private religiosity facilitates social connection and healthy behavior to the same extent as more traditional social and participatory religiosity [6]. In particular, they found that religious individuals (publicly religious in focus) have healthier lifestyles compared to individuals with no religiosity. They also revealed the relationship between public religiosity and a healthy lifestyle—especially in terms of diet/ nutrition. It is true among Danish citizens too [33].
In the Danish community, in more religious cultures, there was a negative correlation between religiosity and health-related risk behaviors associated with a healthier lifestyle. On the contrary, healthier dietary patterns and less smoking were observed in people who had a strong tie to religious practice. Also path analysis and linear regression results, according to Paweł et al. [10] displayed that both spirituality and religiosity and health-related behaviors are positively related. Similarly, another study involving Muslim medical students in Iran showed that religiosity was protective against some unhealthy lifestyle behaviors and some psychological disorders such as depression [34]. This study conducted in Malaysia ascertained ethnicity and religion had adverse effects on health-related issues in general and psychiatric events in focus.
The Islamic religion in Malaysia, in particular, was found to be an important factor that protected the students from unhealthy lifestyle behavior including suicide attempts than Christianity, Hinduism, Buddhism, Taoism, and other religions [35]. However, another study among Jewish medical students found that there was no significant association between religiosity and healthy lifestyles behaviors such as depression, and anxiety [36]. In view of these mixed results, there is a need for more studies in this area to further define the relationship between religion practice and healthy lifestyle behavior. However, the results of related studies about the effect of religion are controversial.
Ample studies also revealed relationships between healthy lifestyle behavior and cognitive function in students [37,38,39]. Maniaci et al. [38] found that academic performance was negatively correlated with unhealthy lifestyle behaviors such as excessive internet use, perceived stress, and bad nutrition in Italian students. Composite scores of healthy lifestyles behavior were a significant predictor of better academic achievement.
More than 42 relevant studies supported that religion plays a causal role in the academic success of students [40]. For instance, in the Muslim dominant community, a study on students of the Islamic Religious Education Study Program disclosed that religiosity is positively and significantly related to student achievement motivation [41]. Similarly, a Christian-dominated population at a university in the United States revealed that religious affiliation and religiosity have an impact on students’ academic performance [9].
In Ethiopia, different studies were conducted in relation to the role of religious institutions in many affairs. For example, Kumilachew [42] has studied the role of churches in the provision of social support three types: emotional support, provision of food, and provision of cloths. In addition, he also reported that religion is inherently a social phenomenon and it has many effects on the socio-economic life of the community. Asselefech [43] has reported a remarkable finding on the role of Ethiopian churches in the development of adult education in Gonder and Addis Ababa. In addition to the aforementioned scholars, Serkalem [44] worked on the use, application, and integration of religious spirituality in clinical social service in Addis Ababa. In her study, she attempted to explore the contribution of religion in the process of helping patients in clinical social services. Tilahun et al. [45] also investigated the contribution of the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahido church to forest management in the North Shewa Zone. Minychel [46] also explores the role of the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahido Church (EOTC) contributes to mitigating the social problem.
The rationale for this research is based on four aspects. First, as we have observed above these studies in Ethiopia, previous researchers reflect or share some knowledge about the role of EOTC on natural resource conservation, mitigating social problems or conflict resolution, adult education, HIV/AIDS, and Health related issues. But, these studies conducted in Ethiopia, also show the same problem; which is focusing only on EOTC religion, which is similar to the previous one. All the above studies conducted in Ethiopia did not investigate about the role of religiosity and spirituality in shaping healthy lifestyle behavior and academic achievement. Second, the review of the previous studies demonstrated that mixed findings about the impact of religious practice. For example, numerous scholars such as Francis et al. [35] found that religious practice is important factor that enhance the students’ healthy lifestyle behavior. However, another study among Jewish medical students found that there was no significant association between religiosity and healthy lifestyles behavior [36]. There is a need for more studies in this area to further define the relationship between religious practice, healthy lifestyle behavior, and academic achievement. Thus, the foregoing scholars’ mixed findings about effects of religiosity motivated this investigation. Third, these three variables haven’t been studied jointly so far across globe. Fourth, this paper is believed to have significance for the officials of Ministry of Education (MoE), students, researchers, spiritual and secular organizations and other relevant stakeholders by increasing knowledge and information on the role religious practice in shaping adolescents’ healthy life style behavior and academic achievement. Based on the results of this study, educational policymakers at the federal level may include the development of religious capital as a means of promoting healthy lifestyle behavior. In addition, understanding healthy lifestyle behavior in adolescents is critical to the development of interventions needed to promote positive behaviors that can prevent negative physical and mental health outcomes, which may have lifelong implications. Thus, the findings of this study will be useful to the university adolescent students to be clear and ready for future life adjustment being religiously oriented and involved in their current life situation settings. Therefore, these initiations made researchers fill the gap by gearing towards the following basic research questions.
- 1.
Is there a significant mean difference among university students in terms of their gender, religion, batch, region, and university regarding religious practice?
- 2.
Is there a significant mean difference among university students in terms of their gender, religion, batch, region, and university regarding healthy lifestyle behavior?
- 3.
Are there any significant relationship between students’ religious practice, healthy life style behavior, and academic achievement?
- 4.
To what extent does students’ religious practice predict their healthy life style behaviors and academic achievement?
- 5.
Does the healthy lifestyle behavior significantly mediate the relationship between religiosity/religious practice and academic achievement in University students?
Theoretical framework
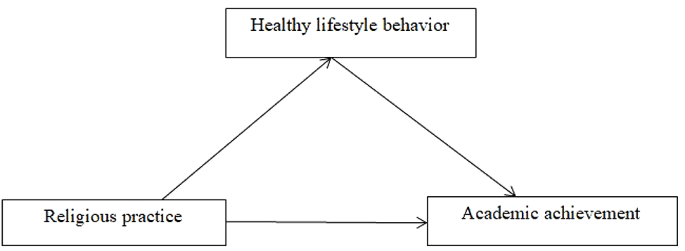
Researchers followed on study demands-resources (SD-R) model to test a model that examines the mediation effect of healthy lifestyle behavior in the relationship between religious practice and academic achievement. This theory is in line with job demands-resources model of Demerouti et al. [47] who stated that study resources (the good social or physical aspects at university) are associated with certain positive outcomes such as psychological and academic benefits. In the same vein, within this SD-R framework, high study resources foster positive outcomes, such as academic performance [48]. The major benefit of SD-R theory or model is that it is much more specific and focused on the university context. The SD-R framework also provides a theoretical basis to investigate the influences of the study context on students’ outcomes such as academic achievement, health and well-being. This model is an outstanding theoretical basis to examine the effects of the study context students’ success such as academic success, health, and well-being [48]. According to Lesener et al.’s [48] SD-R model, environmental resources promote study resources and produce positive study outcomes. This model is explicitly and exclusively validated within the university context. The present study, perceived religious practice (as one of the aspects of the environmental resources) may promote healthy lifestyle behavior (as one facet of study resources) and produce positive academic achievement as one of the study outcomes. The theoretical or conceptual framework is presented in Fig. 1.
Adblock test (Why?)
from "healthy life" - Google News https://ift.tt/06KWeHt
via
IFTTT